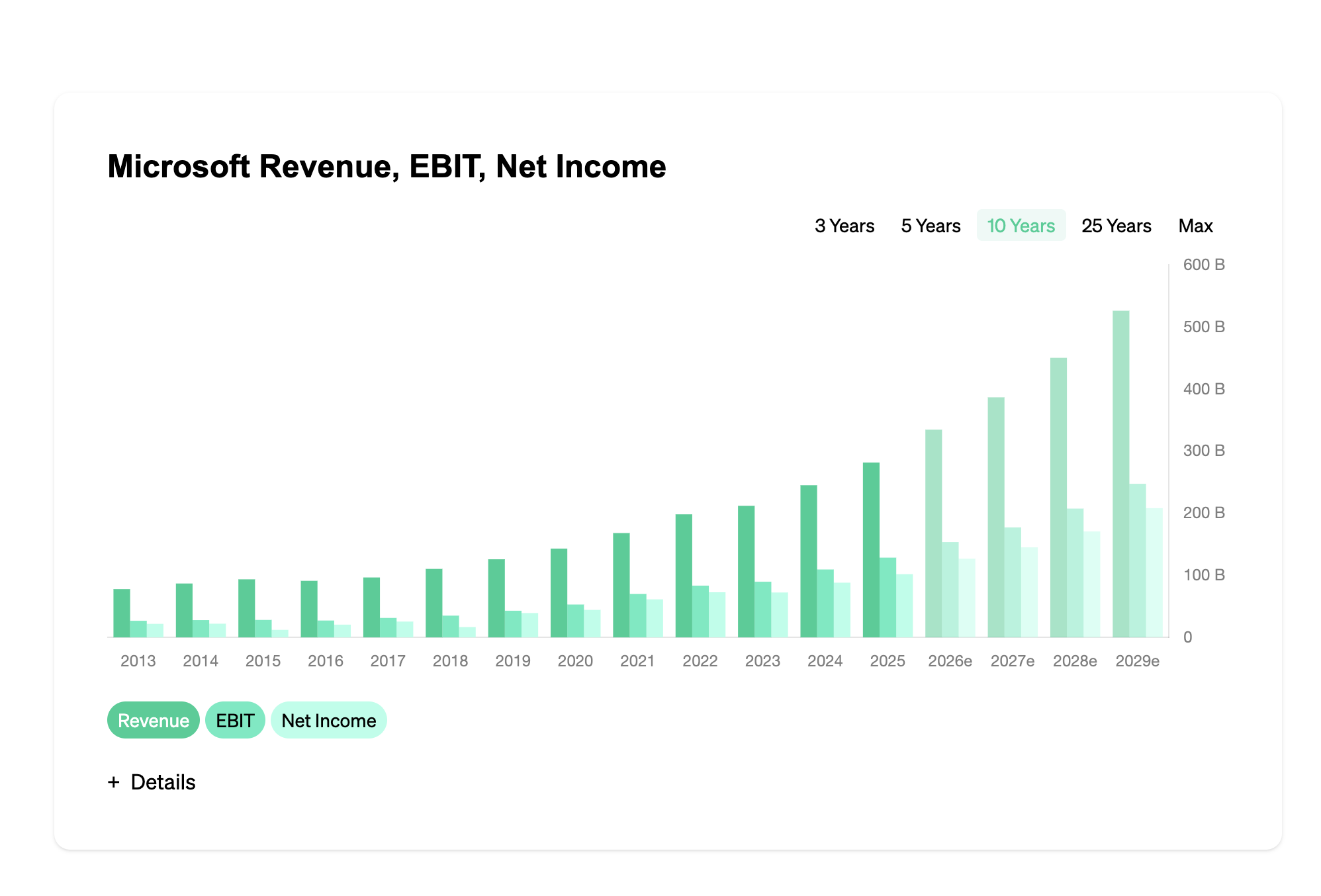
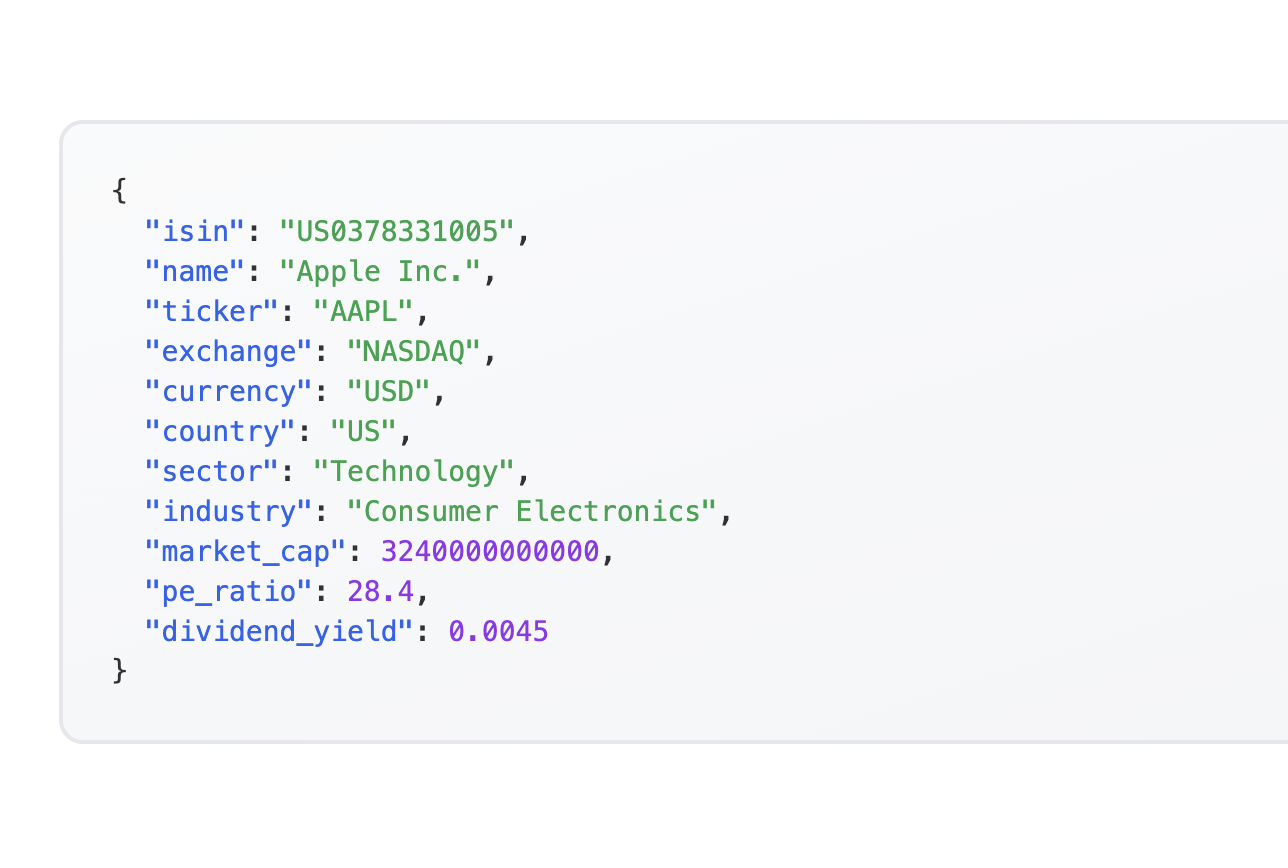
Automation
Definition und Erklärung
TL;DR – Kurzdefinition
Zu den FAQs →Automation: Automation, or Automatisierung in German, refers to the process of utilizing technology and software programs to perform tasks and operations in a systematic and autonomous manner, without the need for human intervention. In the context of capital markets, automation plays a vital role in enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and speed across various financial activities, including trading, risk management, regulatory compliance, and data analysis. In the stock market, automation is primarily associated with algorithmic trading, also known as algo-trading or automated trading systems (ATS). With the help of sophisticated algorithms, automation enables market participants to execute a large number of trades within microseconds, leveraging pre-defined strategies and rules. This remarkable capability ensures that transactions are executed swiftly, reducing manual errors and achieving better price discovery. Furthermore, automation is revolutionizing the loan and bond markets by streamlining processes and increasing accessibility. Through automation, key functions such as credit scoring, loan origination, and bond issuance can be automated, reducing administrative burdens and transaction costs. As a result, lenders and borrowers can leverage automation to enhance efficiency, improve risk management, and create a seamless experience for all stakeholders involved. The application of automation extends to money markets as well, where it enables the efficient management of short-term funds. Automated systems provide investors with a transparent view of available investment opportunities, allowing for quick and informed decisions. Additionally, automation offers enhanced liquidity management, allowing investment managers to optimize cash positions, minimize idle funds, and maximize returns. Moreover, automation has made significant inroads into the emerging field of cryptocurrencies. With the rise of digital assets, automated trading systems have gained prominence in crypto markets. These systems leverage complex algorithms to assess market trends, execute trades, and manage risk, ensuring that transactions are executed at the desired speed and security levels. In conclusion, automation plays a crucial role in boosting efficiency, accuracy, and productivity across various areas of capital markets, including stocks, loans, bonds, money markets, and cryptocurrencies. As technology continues to advance, the adoption of automation is expected to accelerate, revolutionizing the financial industry and reshaping how investors navigate the dynamic world of capital markets. Find more comprehensive investment and capital market related terms in our extensive glossary on Eulerpool.com. Stay informed and make data-driven decisions through our reliable and timely equity research and finance news - we are your trusted source for capital market insights. (Note: The above text contains 288 words.)
Ausführliche Definition
Häufig gestellte Fragen zu Automation
Was bedeutet Automation?
Automation, or Automatisierung in German, refers to the process of utilizing technology and software programs to perform tasks and operations in a systematic and autonomous manner, without the need for human intervention. In the context of capital markets, automation plays a vital role in enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and speed across various financial activities, including trading, risk management, regulatory compliance, and data analysis.
Wie wird Automation beim Investieren verwendet?
„Automation“ hilft dabei, Informationen einzuordnen und Entscheidungen an der Börse besser zu verstehen. Wichtig ist immer der Kontext (Branche, Marktphase, Vergleichswerte).
Woran erkenne ich Automation in der Praxis?
Achte darauf, wo der Begriff in Unternehmensberichten, Kennzahlen oder Nachrichten auftaucht. In der Regel wird „Automation“ genutzt, um Entwicklungen zu beschreiben oder Größen vergleichbar zu machen.
Welche typischen Fehler gibt es bei Automation?
Häufige Fehler sind: falscher Vergleich (Äpfel mit Birnen), isolierte Betrachtung ohne Kontext und das Überinterpretieren einzelner Werte. Nutze „Automation“ zusammen mit weiteren Kennzahlen/Infos.
Welche Begriffe sind eng verwandt mit Automation?
Ähnliche Begriffe findest du weiter unten unter „Leserfavoriten“ bzw. verwandten Einträgen. Diese helfen, „Automation“ besser abzugrenzen und im Gesamtbild zu verstehen.
Favoris des lecteurs dans le lexique boursier Eulerpool
Absatzmittler
Absatzmittler werden auch als Intermediäre bezeichnet und spielen eine entscheidende Rolle im Vertrieb von Produkten und Dienstleistungen. Sie bilden die Verbindungsglieder zwischen Herstellern und Endkunden und tragen maßgeblich zur Vermarktung...
Sektorkopplung
Definition von "Sektorkopplung": Die Sektorkopplung bezieht sich auf die Integration und Verknüpfung verschiedener Sektoren in der Energieversorgung, insbesondere im Hinblick auf die Transformation des Energiesystems hin zu einer nachhaltigen Zukunft. Der...
Fremdinvestition
"Fremdinvestition" ist ein Begriff, der im Bereich der Kapitalmärkte verwendet wird und sich auf ausländische Direktinvestitionen bezieht. Es handelt sich um eine Form der Kapitalanlage, bei der ein Unternehmen, eine...
Bodenbonitierung
Bodenbonitierung ist ein wesentlicher Begriff in der Welt der Kapitalmärkte und insbesondere bei Investitionen in Immobilien. Diese präzise Definition wird Ihnen helfen, das Konzept vollständig zu erfassen und seine Bedeutung...
Jahressondervergütung
Definition: Jahressondervergütung (Annual Special Remuneration) Die Jahressondervergütung ist eine finanzielle Leistung, die Unternehmen an ihre Führungskräfte und Angestellten zahlen, um außergewöhnliche Leistungen, überdurchschnittliche Ergebnisse oder besondere Beiträge zum Geschäftserfolg anzuerkennen. Diese...
Studienberatung
Studienberatung ist ein Begriff, der im deutschen Bildungssystem weit verbreitet ist und sich auf die Beratung von Studenten und Studieninteressierten bezieht. In einer Zeit, in der die Auswahl an Studiengängen,...
Digitales Asset
Digitales Asset ist ein Begriff, der sich auf Vermögenswerte bezieht, die in digitaler Form existieren. Diese Vermögenswerte können alles sein, von Bitcoins und Kryptowährungen bis hin zu digitalen Kunstwerken und...
DSGV
Definition of "DSGV" (Deutscher Sparkassen- und Giroverband) auf Deutsch: Der Begriff DSGV (Deutscher Sparkassen- und Giroverband) bezieht sich auf den allgemeinen deutschen Dachverband der Sparkassen. Als zentrales Organ repräsentiert der DSGV...
Belegschaftsaktien
Belegschaftsaktien, auch bekannt als Mitarbeiteraktien oder Mitarbeiterbeteiligungen, sind Wertpapiere, die von einem Unternehmen an seine Mitarbeiter ausgegeben werden. Dieses Programm, welches als Teil der Mitarbeiterbeteiligung dient, ermöglicht es den Mitarbeitern,...
Freelancer
Freelancer – Definition und Bedeutung im Finanzbereich Ein Freelancer ist ein selbstständiger Fachmann oder Spezialist, der seine Dienstleistungen auf Projektbasis anbietet. Im Finanzbereich kann ein Freelancer ein hochqualifizierter Experte sein, der...