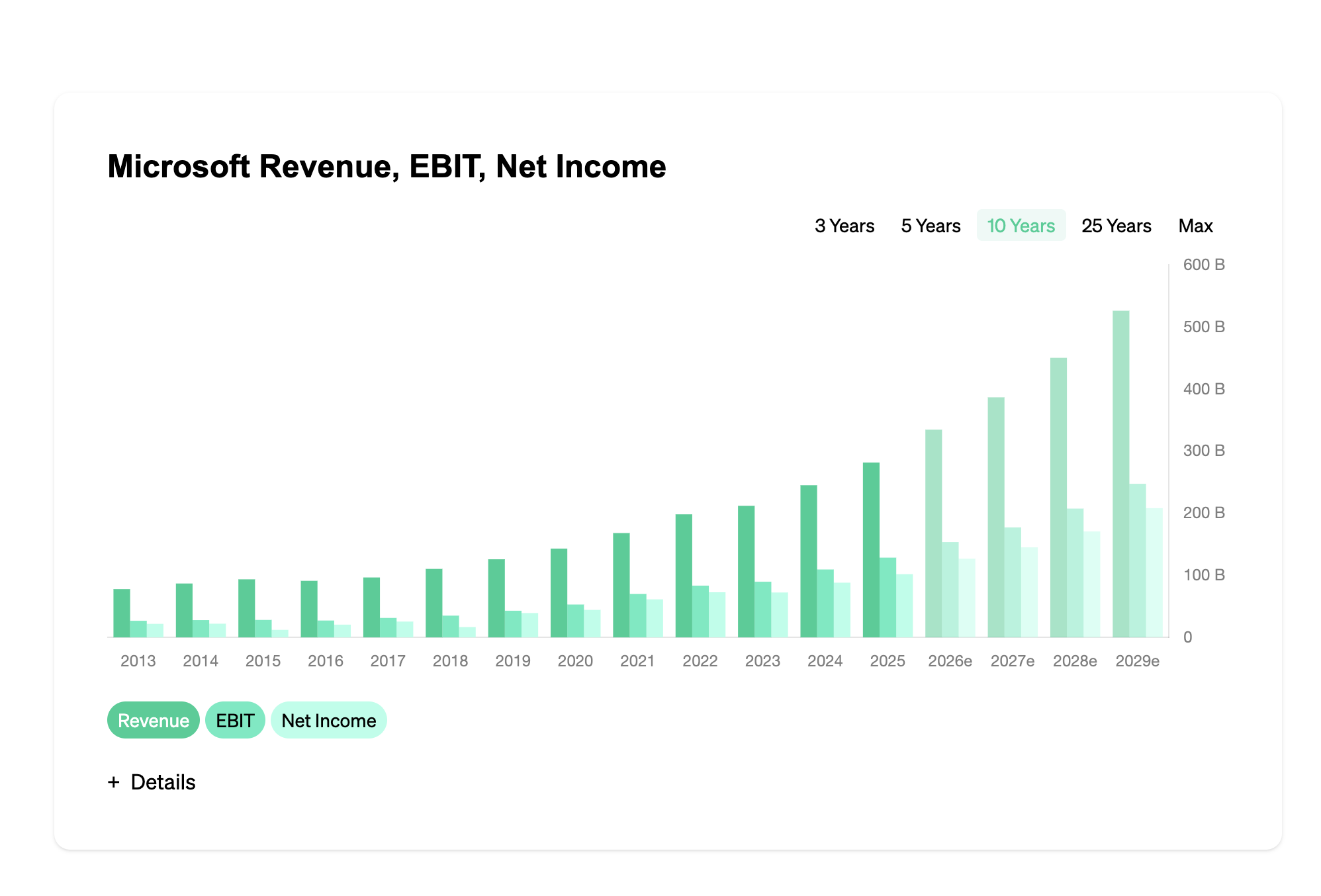
Design for Environment
Definition und Erklärung
TL;DR – Kurzdefinition
Zu den FAQs →Design for Environment: Design for Environment (DfE), or Umweltdesign in German, is a strategic approach that aims to integrate environmental considerations into the design and development of products, processes, and systems. This concept encompasses the entire product lifecycle, from the extraction of raw materials to the disposal or recycling of the end product. Implemeting DfE involves the use of innovative design techniques, technologies, and materials that minimize the negative environmental impacts associated with a product or process. It seeks to achieve a sustainable balance between ecological, economic, and social factors. One of the primary goals of DfE is to reduce the consumption of resources and energy during the manufacturing stage. This can be achieved through the adoption of lightweight materials, efficient production methods, and the integration of renewable energy sources. By optimizing the design, products can be manufactured with fewer materials and energy requirements, resulting in reduced carbon emissions and a lower ecological footprint. Furthermore, DfE emphasizes the importance of selecting environmentally friendly materials that can be easily recycled or disposed of without causing harm to the environment. This involves considering factors such as biodegradability, recyclability, and the presence of hazardous substances in the material composition. In addition to minimizing negative impacts, DfE also encourages the incorporation of positive environmental attributes into products. Examples include the use of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient features, and the facilitation of product repair, reusability, or upgradability. By integrating DfE principles into the design process, companies can gain a competitive advantage by meeting evolving market demands for environmentally conscious products. Consumers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability when making purchasing decisions, and products designed with the environment in mind are more likely to appeal to these conscious customers. The implementation of DfE can also lead to cost savings for companies in the long run. By optimizing design and material choices, companies can reduce production costs, improve energy efficiency, and lessen waste generation. Moreover, adherence to environmental regulations and standards can protect companies from potential fines and penalties. In conclusion, Design for Environment is a comprehensive approach that ensures the integration of sustainability principles into the design and development of products, processes, and systems. By considering environmental factors throughout the entire product lifecycle, companies can create innovative, eco-friendly products that benefit both the environment and their bottom line. At Eulerpool.com, we aim to provide investors in capital markets with a comprehensive glossary that covers essential terms in stocks, loans, bonds, money markets, and crypto. Our glossary is designed to be a valuable resource for both beginners and professionals in the finance industry. Stay tuned for the launch of our glossary on Eulerpool.com, where you will find accurate, reliable, and up-to-date information to enhance your understanding of the complex world of finance.
Ausführliche Definition
Häufig gestellte Fragen zu Design for Environment
Was bedeutet Design for Environment?
Design for Environment (DfE), or Umweltdesign in German, is a strategic approach that aims to integrate environmental considerations into the design and development of products, processes, and systems. This concept encompasses the entire product lifecycle, from the extraction of raw materials to the disposal or recycling of the end product.
Wie wird Design for Environment beim Investieren verwendet?
„Design for Environment“ hilft dabei, Informationen einzuordnen und Entscheidungen an der Börse besser zu verstehen. Wichtig ist immer der Kontext (Branche, Marktphase, Vergleichswerte).
Woran erkenne ich Design for Environment in der Praxis?
Achte darauf, wo der Begriff in Unternehmensberichten, Kennzahlen oder Nachrichten auftaucht. In der Regel wird „Design for Environment“ genutzt, um Entwicklungen zu beschreiben oder Größen vergleichbar zu machen.
Welche typischen Fehler gibt es bei Design for Environment?
Häufige Fehler sind: falscher Vergleich (Äpfel mit Birnen), isolierte Betrachtung ohne Kontext und das Überinterpretieren einzelner Werte. Nutze „Design for Environment“ zusammen mit weiteren Kennzahlen/Infos.
Welche Begriffe sind eng verwandt mit Design for Environment?
Ähnliche Begriffe findest du weiter unten unter „Leserfavoriten“ bzw. verwandten Einträgen. Diese helfen, „Design for Environment“ besser abzugrenzen und im Gesamtbild zu verstehen.
Reader Favorites in the Eulerpool Stock Market Lexicon
Global Marketing
Globales Marketing bezeichnet eine umfassende Marketingstrategie, die multinationalen Unternehmen dabei hilft, ihre Produkte und Dienstleistungen weltweit zu vermarkten. Es ist ein strategischer Ansatz, der darauf abzielt, die Bedürfnisse und Wünsche...
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) – Definition und Erklärung Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) oder alternative Streitbeilegung ist ein Verfahren zur Lösung von Streitigkeiten zwischen Parteien außerhalb des traditionellen Gerichtssystems. Es bietet den...
Anfangsbilanz
Anfangsbilanz ist ein entscheidendes finanzielles Instrument zur Bewertung des Vermögens und der Schulden eines Unternehmens zu Beginn eines Geschäftsjahres oder einer bestimmten Geschäftsperiode. Sie ist auch als Eröffnungsbilanz oder Startbilanz...
Diskettenlaufwerk
Diskettenlaufwerk ist ein Begriff, der sich auf ein Peripheriegerät bezieht, das in der Vergangenheit in Computern weit verbreitet war. Es handelt sich um ein Gerät, das entwickelt wurde, um Disketten...
Bankenstimmrecht
Bankenstimmrecht ist ein Begriff, der sich auf das Stimmrecht von Banken in Bezug auf Aktiengesellschaften bezieht. Es bezieht sich hauptsächlich auf finanzielle Institutionen wie Banken und Versicherungsunternehmen, die erhebliche Anteile...
Handelssteuern
Handelssteuern sind Gebühren oder Abgaben, die beim Handel mit verschiedenen Arten von Wertpapieren und Finanzinstrumenten erhoben werden. Diese Steuern werden von staatlichen Behörden oder Regierungen in verschiedenen Ländern erhoben, um...
Zolllagerverfahren
Zolllagerverfahren bezeichnet ein verwaltungstechnisches Verfahren, das von Zollbehörden angewendet wird, um den Handel mit Waren in speziell designten Lagern zu erleichtern. Dieses Verfahren ermöglicht es Unternehmen, ihre importierten Güter vorübergehend...
Urproduktion
Urproduktion ist ein Begriff aus der Volkswirtschaftslehre, der sich auf die Rohstoffproduktion bezieht. Der Begriff "Urproduktion" wird auch als "Primärproduktion" oder "Extraktionsindustrie" bezeichnet. Es handelt sich um die Gewinnung von...
Push-System
Das Push-System ist ein Begriff, der im Zusammenhang mit elektronischen Plattformen und Finanzmärkten verwendet wird. Es bezieht sich auf ein System, das Echtzeitinformationen an die Nutzer sendet, anstatt dass diese...
Preisfairness
Preisfairness verweist auf das Konzept der gerechten Bewertung von Vermögenswerten, insbesondere im Rahmen von Handelsaktivitäten an den Kapitalmärkten. Es bezieht sich auf die Vorstellung, dass die Preise von Wertpapieren, Anleihen,...